Tokenisation
To search in the page use Ctrl+F on your keyboard
In regard to securing payments, tokenisation is the process of replacing the card number (PAN), a sensitive data, by an alternative unique value named “token”. This process preserves the safety of payment data when performing transactions since it avoids the usage and storage of the original card information.
There are two types of tokenisation on Worldline Sips:
-
Merchant token (or PAT token):
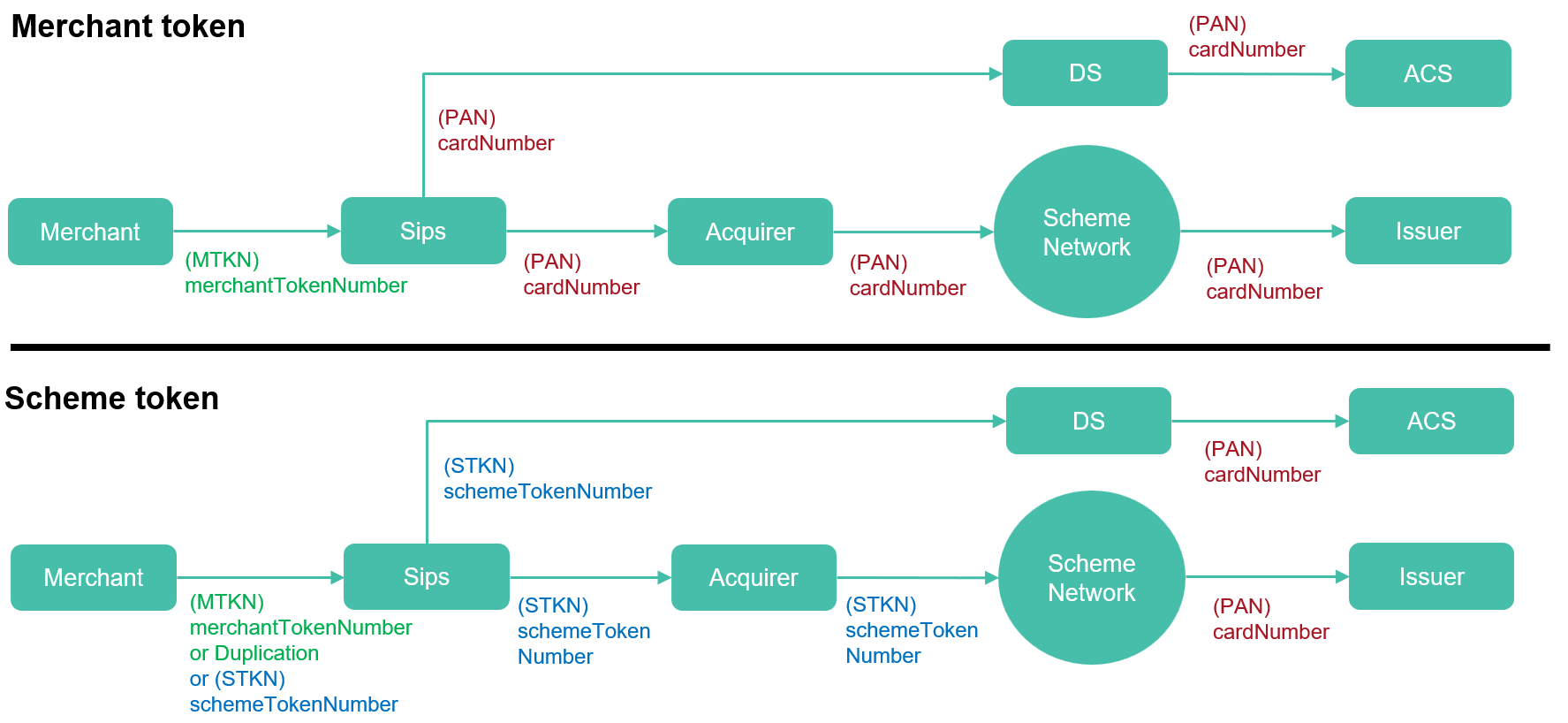
- The card number (PAN) is collected by Worldline Sips who turns it into a merchant token, then securely stores it while complying with all regulations and best practices.
- This reference to the stored card (= token) is sent to you. It does not contain any sensitive nor regulated data.
- You create new payments or refunds using this reference. Worldline Sips transforms it into a PAN during the transaction acceptance.
- Main objective: Reduction of the PCI perimeter of the merchant.
-
Scheme token (also known as network token):
- Scheme tokenization aims to ensure greater security on the payment chain. It applies to card-on-file use cases, in other words as soon as you store cardholder card data for a future use.
- The card data are used to request a Token Service Provider (TSP) to generate a scheme token.
- The scheme token references the real card which will be used to perform the payment. The token expiry date differs from the card one. The scheme token lifecycle can be handled by the emitter and the TSP, as well as you, who can for example suspend or reactivate it.
- The interactions with the acquirer for authorizations and settlements are carried out using the scheme token. The scheme detokenises the scheme token to retrieve the PAN that will be used to interact with the issuer.
-
There are two types of scheme tokens:
- the ones linked to a device (e.g. Apple Pay, …) usable by all merchants,
- the ones defined by and limited to a merchant (or brand).
- Main objective: end-to-end encryption of card data, from the merchant to the scheme, by ensuring a better control over card storage.
- Advantages: ability to ensure the continuity of payments, even in the events of card loss, theft or expiration.
| subject | Merchant token | Scheme token |
|---|---|---|
| Perimeter | ||
| Scheme | CB, VISA, MASTERCARD, AMEX | CB, VISA, MASTERCARD |
| CB Cobadging |
Corresponds to all schemes 1 PAN = 1 merchantToken for CB, VISA and MASTERCARD |
Mono-scheme 1 scheme = 1 schemeToken The scheme token corresponds to the scheme selected to perform the CIT having generated the scheme token A second scheme token can be generated with the same PAN, if a new strongly authenticated CIT is performed using the other scheme of the card |
| orderChannel | Internet, Inapp, MOTO | |
| Transactions types | Subscription and multiple MIT, and OneClick CIT | |
| Supported acquirers | All acquirers |
Authorization protocol CB2A 1.6.1 required Contact Worldline to get the acquirers list |
| Token lifecycle management | ||
| Events notification (deletion, renewal, etc.) | N/A | Into the hands of the emitter, the TSP (Token Service Provider), and the merchant |
| PAN renewal |
can eventually be managed by the merchant via the card updater service only available for CB on Worldline - depends on the consent given by the cardholder to its issuer |
Automatically managed by the scheme token service |
| Compliance | ||
| PCI DSS | Yes (assumed by Worldline Sips) | Yes (assumed by the scheme) |
| DSP2 | Yes (the same rules apply) | |
| Non-sensitive PAN alias | merchantToken (tokenPAN field) | schemeTokenReference (schemeTokenReference field) |
| PAN access | Yes (token2Pan function) | No (PAN only known from the issuer) - possibility to fetch the last 4 digits and the expiry date for display |
| Activation | ||
| Contractualization | with Worldline Sips | with Worldline Sips and the acquirer |
| Enrolment and activation | with Worldline Sips | with Worldline Sips, the scheme(s) and the acquirer |
| Implementation | ||
| Worldline Sips interface | Sips Office | |
| Implementation |
2 implementation modes:
|
3 implementation modes:
|
| Token format |
|
|